Identification and Attribution Analysis of Weak Branches Based on Graph Deep Learning
-
摘要: 电力系统多样化的运行方式对薄弱支路辨识的速度与拓扑泛化性提出更高要求。结合图深度学习及解释方法对薄弱支路进行辨识与溯因分析。采用基于初始残差和单位映射的图卷积神经网络(graph convolutional network via initial residual and identity mapping,GCNII)搭建薄弱支路辨识模型,模型可基于拓扑关系聚合元件特征,结合邻近电网的安全态势评估支路的薄弱程度。采用基于互信息优化的解释方法分析辨识模型的决策依据,提取薄弱支路的主导因子。IEEE68节点系统、实际电网算例结果表明,辨识模型具有较好的辨识准确性和拓扑泛化性,溯因分析结果符合传统机理认知所得结论,可为连锁故障的实时预警和预防控制提供有效指导。Abstract: The diversified mode of power system operation puts forward higher requirements for speed and topological generalization of weak branch identification. In this paper, graph deep learning and interpretation method are used to identify and analyze the weak branches. A weak branch identification model based on graph convolutional network via initial residual and identity mapping (GCNII) is constructed. The model can integrate feature based on topological relation, and evaluate the weakness of branches based on security situation of neighboring power grids. The interpretation method based on mutual information optimization is used to analyze the decision basis of the identification model and extract dominant factors of weak branches. The results of IEEE68 system and actual power grid example show that the identification model has preferable accuracy and topological generalization. The results of attribution analysis are consistent with the conclusions of traditional mechanism cognition, which can provide effective guidance for real-time warning and preventive control of cascading failure.
-
Keywords:
- power system /
- cascading failure /
- weak branch /
- graph deep learning
-
0. 引言
伴随电网互联规模扩大和新能源占比增加,多样化的拓扑结构与潮流状态为安全态势的分析带来挑战。连锁故障常源于薄弱支路的开断,并在低安全水平的运行方式下传播迅速、难以阻断,造成严重损失[1-4]。迫切需要基于潮流状态的空间分布辨识薄弱支路、剖析薄弱原因,为连锁故障的实时预警和预防控制提供依据。
传统的连锁故障薄弱支路辨识方法主要分为两大类:第一类采用概率性或确定性方法基于连锁故障演化规律辨识薄弱支路,如熵理论[5-6]、能量函数理论[7]、连锁故障模拟法[8-10]、风险评估理论[11-12]等,但概率性方法易引发组合爆炸问题,确定性方法依赖于物理特性建模的精确度,上述方法受计算成本的限制而难以实时应用;第二类方法利用复杂网络理论构建计及电网拓扑结构的支路薄弱度指标,如改进介数法[13-15]、最大流理论法[16]和对偶图法[17-18]等,上述方法常基于固定拓扑结构对抽象元件进行建模,难以适应实时运行场景。在计算成本与建模精确度的限制下,传统物理机理方法的速度和精度较难同时保证。
运行方式的不确定性提高了大电网安全态势的分析难度,推动了数据驱动方法在薄弱支路辨识中的应用。文献[19-20]基于强化学习在线搜索风险故障链以评估电网脆弱性,文献[21]构建基于直流潮流的神经网络模型,实现不确定场景下的N−1快速校核。数据驱动方法基于特征提取实现规律拟合,可有效克服不确定性建模精确度有限、传统机理方法时效性不足的缺点,但部分算法因拓扑泛化性、决策透明度不足而无法广泛、可靠地应用。
图深度学习可对关系型数据进行特征挖掘,为增强数据驱动模型的拓扑泛化性提供了新的思路[22-23]。文献[24]基于图卷积神经网络(graph convolutional network,GCN)构建快速潮流计算模型,文献[25]基于深层图卷积神经网络实现配电网拓扑结构的建模和故障位置的辨识,通过对比实验与可视化证明了模型的鲁棒性。上述研究按拓扑关联聚合元件特征,有助于提高模型的拓扑泛化性。
为揭示“黑箱”模型的决策依据,已有相关研究对深度学习可解释方法在电力系统中的应用进行了初步探索。文献[26]使用模型无关的可解释方法(local interpretablemodel-agnostic explanations。LIME)提取了暂态功角稳定预测结果的关键影响因素,文献[27]基于可解释代理模型分析了与静态电压稳定水平强相关的状态变量,文献[28]基于沙普利值加性解释方法(shapley additive explanations,SHAP)提取了影响暂态电压稳定结果的特征并量化其贡献度,文献[29]利用图神经网络和分层关联传播算法实现了连锁故障的预测与重要特征的提取。上述研究通过提取与输出结果强相关的输入特征展示模型的决策依据,有助于提高模型的决策透明度。
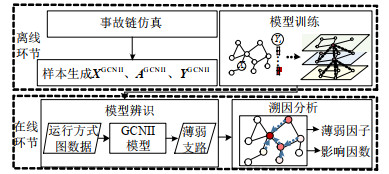
为使薄弱支路的辨识兼顾速度与精度,提高拓扑泛化性与决策透明度,本文提出基于图深度学习的连锁故障薄弱支路辨识与溯因分析方法。采用基于初始残差和单位映射的图卷积神经网络搭建薄弱支路辨识模型,用含多种拓扑结构和潮流状态的图数据样本训练模型,用基于互信息优化的解释方法分析辨识模型的决策依据,提取薄弱支路的主导因子并量化其贡献程度。IEEE68节点系统、实际电网算例结果表明,模型具有较好的准确性、拓扑泛化性,溯因分析结果符合传统机理认知所得结论,可为连锁故障实时预警和预防控制提供有效指导。
1. 薄弱支路的辨识模型
“过载主导型”连锁故障中,故障源支路的薄弱程度是其功率转移冲击力与邻近电网支撑能力间动态平衡性的体现。本文基于潮流状态的空间关系,考察电网安全裕度与功率冲击强度对故障损失的共同影响,基于图深度学习算法构建短时间尺度连锁故障的薄弱支路辨识模型。
1.1 电网图数据构建
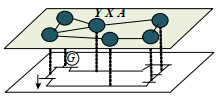
按拓扑关系组织元件特征生成电网图数据样本。为使模型的信息传递机制适用于解释方法,将节点作为基本计算单元,用于特征存储、数值计算、结果输出,而边仅用于表征节点的拓扑关联、传递节点的特征信息。
上述计算机制下,按图 1所示生成样本拓扑以满足对支路薄弱属性的考察,将电网域“支路”映射为图域G的“节点”,将“母线”映射为“边”。存储样本数据以支持非线性关系Y=f(X,A)的拟合,其中节点特征矩阵X∈R N×d为N个节点的d维输入特征,邻接矩阵A∈[0,1] N×N描述节点的连接关系,Y∈R N×F为N个节点的F维输出结果。
因连锁故障的功率转移路径难以求解,而单母线所有出线更易互为替代输电通道,其对应节点在G中经多条边两两相连,使模型较易对目标支路的功率转移路径进行特征提取。因电网域各元件间的交互影响程度与拓扑关联紧密度呈正相关,图域各中心节点协同计算时,信息交互强度取决于节点的连接关系,故G可提高拓扑相近的元件信息在图域中的互通频率,使模型对中心支路的邻近元件特征按不同拓扑距离实现层次化提取。
1.2 改进的图神经网络
连锁故障在发展初期通常仅波及故障源的邻近电网[30],故利用具备局部感知野的卷积神经网络提取支路的邻接元件特征,结合邻近电网安全态势评估中心支路的薄弱程度。
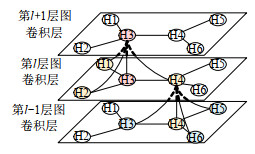
受关系型数据对平移不变性的限制,图数据无法用于普通卷积神经网络。图卷积神经网络(graph convolutional network,GCN)可打破该限制,在非欧空间中借助谱图理论(spectral graph theory)实现图数据的卷积运算。GCN将空域图信号f、h经傅里叶变换F(⋅)映射到频域中进行点积后,经逆变换再返回空域,构建如下卷积框架:
(f∗h)=F−1[F{f}⋅F{h}] (1) 基于式(1)的理论框架,GCN将f、h替换为节点特征矩阵与卷积核参数,形成如下运算规则:
H(l+1)=f(H(l),A)=σ(˜D−1/2˜A˜D−1/2H(l)W(l)) (2) 式中:H(l+1)、H(l)表示第l+1、l层的节点特征;W(l)为第l层待训练的权重参数;˜A=A+IN,A为N个节点的邻接矩阵;IN为单位矩阵;˜D为˜A的节点度矩阵;˜D−1/2˜A˜D−1/2为归一化后的拉普拉斯矩阵,反应邻接节点特征扰动时产生的累积信息增益,用于刻画局部平滑度;σ(⋅)为激活函数。由图 2可知,GCN中的信息沿边递归地进行传递,节点仅通过邻边提取信息,信息提取范围可随网络叠加而逐层扩大、随拓扑变化而动态调整,故节点的信息感知域易于控制且具有拓扑适应性。
为提升模型性能,需扩大信息感知域,但深层GCN模型因过度平滑、信息丢失问题而性能较差。鉴于此,文献[31]使用基于初始残差和单位映射的改进图卷积神经网络GCNII构建深层模型。GCNII网络的运算规则如下所示:
H(l+1)=σ{[(1−αl)˜D−1/2˜A˜D−1/2H(l)+αlH(0)][(1−βl)IN+βlW(l)]} (3) 与式(2)相比,GCNII在每层引入待学习的单位映射参数βl和初始残差连接参数αl,提升模型的性能。
1)GCNII的残差连接可缓解深层模型的过度平滑问题。随着网络层数的增加,GCN会产生懒惰随机游走现象,使结果收敛到固定值,产生过渡平滑现象;而GCNII将第l层激活的H(l)通过˜D−1/2˜A˜D−1/2进行平滑表示后,与αlH(0)相加,共同作为第l+1层的输入,可缓解过渡平滑的问题。
2)GCNII的单位映射可防止模型在收敛过程中丢失信息。文献[32]从理论上证明了GCN的特征会收敛到子空间而造成信息丢失;而GCNII引入(1−βl)IN+βlW(l),减小了参数W(l)的范数,通过强正则化避免了过拟合现象,减缓了收敛速度,可减少信息的损失。
3)GCNII引入参数βl可学习邻接矩阵A包含的拓扑信息。GCN本质上模拟了一个固定的K阶多项式滤波器,该滤波器将使结果只收敛于输入特征X中的信息分布;而GCNII引入参数βl,可以表达任意参数θl下的K阶多项式滤波器:
h(K)=(K∑l=0θlPl)x (4) 式中:Pl=IN−˜D−1/2˜A˜D−1/2与邻接矩阵A包含的拓扑信息有关;x为输入特征X中的向量;GCNII通过更新参数βl,使结果可收敛于从输入特征X和邻接矩阵A中同时学习到的信息分布。
1.3 连锁故障薄弱支路的辨识模型
基于GCNII构建薄弱支路辨识模型,仿真短时间尺度连锁故障,根据事故链生成样本并训练模型。
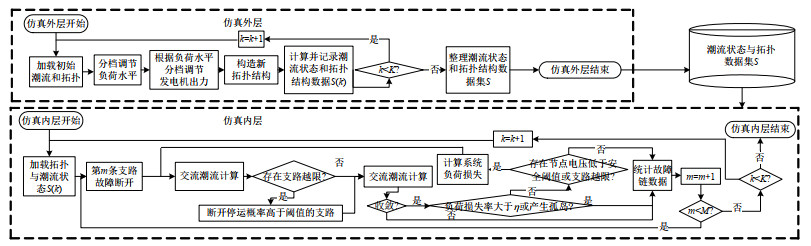
首先,由图 3所示步骤对连锁故障进行仿真。仿真外层模拟新能源机组、可调节负荷投入及支路检修时的潮流状态,无故障断开0、1、2条支路,并分档随机调整负荷量、发电量及无功注入功率;仿真内层模拟外层潮流状态下的短时间尺度连锁故障,包含如下仿真策略。
1)初始支路开断策略:初始潮流状态下,遍历仿真所有支路开断触发的连锁故障。
2)紧急减载控制策略:模拟调度中心的连锁故障阻断控制,支路负载过重、母线电压过低时分别启动支路越限减载、母线低压减载控制,切除部分负荷使支路功率、母线电压恢复至安全值。基于最优潮流模型,参考文献[33]计算最小的减载控制代价,作为负荷损失结果。
3)支路跳闸规则:模拟支路严重越限时的继电保护动作,使用过负荷累计函数Ak(t,Δt)描述支路k在t至t+Δt时刻的过负荷严重程度[34]:
Ak(t,Δt)={∫t+Δtt(Fk(t)−Ck)3 dt,Fk(t)>Ck0, 其他 (5) 式中:Fk(t)为支路k在t时刻的功率值;Δt为支路k由出现严重越限到保护动作实施的时间间隔;Ck为人工设置的阈值。当累积值Ak经Tk秒超过临界值Ak,limit时,迅速断开支路k,本文取Ak,limit为有功功率超过热稳定极限值的40%且持续5s时的累计值,设Tk⩽。
其次,整理故障链生成图数据样本XGCNII、AGCNII、YGCNII。构建节点特征XGCNII描述母线、支路的潮流状态:
{\boldsymbol X^{{\text{GCNII}}}} = [{x^P},{x^Q},{x^{\Delta U}},{x^{\Delta \theta }},{x^{{P_{{\text{limit}}}}}},{x^{{U_{j,{\text{limit}}}}}}] (6) 式中: {x^P} 为支路有功功率,描述支路功率转移的潜在冲击强度; {x^{{U_{j,{\text{limit}}}}}} 表示支路末端电压Uj与极限值(0.95pu或1.05pu)的最小差值,描述母线电压安全裕度; {x^Q} 、 {x^{\Delta U}} 表示支路无功功率和首末端电压幅值差,与 {x^P} 、 {x^{{U_{j,{\text{limit}}}}}} 共同刻画支路电压降落程度[35]; {x^{{P_{{\text{limit}}}}}} 表示支路有功功率与热稳定极限的差值,描述支路的剩余有功传输能力; {x^{{\theta _{ij}}}} 表示支路首末端电压相角差,反映潮流均衡度[36]。
构建关联矩阵 {\boldsymbol A^{{\text{GCNII}}}} \in {[{\text{0,1]}}^{{\text{ }}N \times N}} 描述包含N条支路的电网拓扑结构,其元素表示为
{A}_{ij}=\left\{\begin{array}{c}1\text{ , }节点i与节点j有拓扑连接\\ 0\text{ , }节点i与节点j无拓扑连接\end{array}\right. (7) 按支路开断对安全态势的不同损害程度,将支路薄弱度划分为8类,如表 1所示。电网结构完整且潮流未崩溃时,用控制代价Lcut描述电压跌落、支路过载的严重程度[37],Lcut为事故链的负荷累积损失量与故障前总负荷量的比值。输出矩阵 {\boldsymbol Y^{{\text{GCNII}}}} \in {\boldsymbol R^{N \times 8}} 的元素表示为
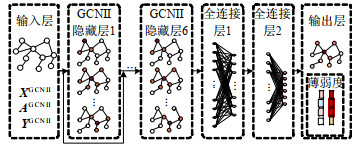
{Y}_{ij}=\left\{\begin{array}{l}1\text{ , }支路i薄弱程度属于第j类\\ 0\text{ , }支路i薄弱程度不属于第j类\end{array}\right. (8) 表 1 薄弱程度的划分Table 1. Partitioning of weakness薄弱程度 连锁故障事故后果 薄弱程度 连锁故障事故后果 1 无失负荷情况 5 0.15 < Lcut≤0.2 2 0 < Lcut≤0.05 6 无孤岛产生且Lcut > 0.2 3 0.05 < Lcut≤0.1 7 有孤岛产生且Lcut > 0.2 4 0.1 < Lcut≤0.15 8 潮流崩溃 将上述样本经标准化处理后用于训练模型{\boldsymbol Y^{{\text{GCNII}}}} = f({\boldsymbol X^{{\text{GCNII}}}},{\boldsymbol A^{{\text{GCNII}}}}),训练过程中,使用负对数似然(negative log-likelihood,NLL)计算损失函数,针对每种薄弱程度类别z分别设置损失权重 {\omega _z} (z=1, …, 8),以避免有偏样本的影响;使用Adam优化器根据反向传播的梯度信息更新参数 {\beta _l} 和 {W^{(l)}} ,初始学习率设为0.005,批尺寸(batch size)设为32。使用验证集寻找最优的网络层数及超参数 {\alpha _l} 。模型结构如图 4所示,包含6个GCNII层、2个全连接层和1个softmax层,激活函数设为PReLU。
2. 薄弱支路的溯因分析
辨识模型的决策机制经参数训练得以确定,为掌握该机制下模型的决策依据,结合图 2所示的信息传递过程,基于互信息优化提取与辨识结果强相关的节点特征并量化其贡献程度,构建支路的薄弱原因。
已知节点集合Gc与节点特征Xc,模型Φ针对节点i的输出结果为y(i)=Φ(Gc, Xc)。将Gc中对y(i)贡献度较高的节点构成关键节点集Gs,将关键节点各自贡献度较高的特征构成关键节点特征集XsF。使用互信息(mutual information,MI)度量模型Φ的联合输入变量(Gs, XsF)与输出y(i)之间的共有信息含量,表示为MI(y(i), (Gs, XsF)),当该互信息最大时,即可将Gs、XsF作为模型Φ的决策依据。
参考文献[38],构建互信息优化模型如下所示:
\mathop {\max }\limits_{{G_{\text{s}}},X_{\text{s}}^{\text{F}}} {M_{\text{I}}}(Y,({G_{\text{s}}},X_{\text{s}}^{\text{F}})) = H(Y) - H(Y|G = {G_{\text{s}}},X = X_{\text{s}}^{\text{F}}) (9) 式中: {G_{\text{s}}} \subseteq {G_{\text{c}}} 、 X_{\text{s}}^{\text{F}} = \{ x_j^{\text{F}}|{i_j} \in {G_{\text{s}}}\} 为待优化的变量;Y为模型Φ输出结果y的条件分布; H( \cdot ) 为针对离散量的熵计算。因模型Φ的参数经训练已确定,熵 H(Y) 为常数,故式(9)等价于最小化条件熵 H(Y|G = {G_{\text{S}}},X = X_{\text{S}}^{\text{F}}) ,将式(9)改写为
\begin{array}{l} {\text{min[}}H(Y|G = {G_{\text{s}}},X = X_{\text{s}}^{\text{F}}){\text{]}} = \hfill \\ \ \ \ \ {\text{ min[}} - \sum\limits_{c = 1}^C {1(y = c)} \lg P(Y = y|G = {G_{\text{s}}},X = X_{\text{s}}^{\text{F}}){\text{]}} \hfill \\ \end{array} (10) 式中 P( \cdot ) 、C分别为模型输出结果y的分布和类别总数。基于式(10)进行优化,可最大程度保留特征的组合效应,获得与模型Φ输出结果间互信息最大的Gs、XsF,即模型的决策依据。
将上述互信息优化方法应用于辨识模型ΦGCNII和样本XGCNII、AGCNII、YGCNII,修改式(10)的优化过程,分别提取关键节点和关键节点特征。
1)通过互信息优化学习边的信息权重M,用以提取关键节点集Gs。引入结构掩码 \sigma (\boldsymbol M) ,设Gs为 {\boldsymbol A^{{\text{GCNII}}}} \odot \sigma (\boldsymbol M) 并代入式(10),以M为优化变量,寻找最符合模型结果的边信息权重:
\left\{\begin{array}{l}\text{min[}-{\displaystyle \sum _{c=1}^{C}1(y=c)}\mathrm{lg}P(\boldsymbol Y=y|G={\boldsymbol A}^{\text{GCNII}}\odot \\ \sigma (\boldsymbol M),\boldsymbol X={\boldsymbol X}^{\text{GCNII}})\text{]}\end{array}\right. (11) 式中:N为节点总数; \boldsymbol M \in {R^{N \times N}} 为待优化的边信息权重矩阵;Sigmoid函数 \sigma ( \cdot ) 将M映射为掩码矩阵 {[0,1]^{N \times N}} 。基于M的优化结果,筛选并保留AGCNII中高信息权重的边,生成关键节点集Gs。
2)考察Gs中节点所含d维特征的贡献度,学习节点特征信息权重 \boldsymbol F \in {R^{N \times d}} 。引入特征掩码 \sigma (\boldsymbol F) ,设关键节点特征集XsF为 {\boldsymbol X^{{\text{GCNII}}}} \odot \sigma (\boldsymbol F) 并代入式(10),寻找最优的特征信息权重矩阵F:
\left\{ \begin{array}{l} {\text{min[}} - \sum\limits_{c = 1}^C {1(y = c)} \lg P(\boldsymbol Y = y|G = {G_{\text{s}}}, \hfill \\ \boldsymbol X = {\boldsymbol X^{{\text{GCNII}}}} \odot \sigma (F)){\text{]}} \hfill \\ \end{array} \right. (12) 为使特征在数值上具有比较性,将 {\boldsymbol X^{{\text{GCNII}}}} \odot \sigma (F) 表示为 \boldsymbol Z + ({\boldsymbol X^{{\text{GCNII}}}} - \boldsymbol Z) \odot \sigma (\boldsymbol F) ,Z是从经验边际分布中抽样的d维随机变量,当样本数不足时可人为进行设置[39]。基于优化结果F,筛选并保留高信息权重的节点特征,生成关键节点特征集XsF。
最后,基于模型决策依据XsF、Gs和F,对薄弱支路进行溯因分析。因功率转移和电压跌落共同推动连锁故障的发展,将XsF归纳为4种薄弱因子:有功功率裕度偏小、有功功率偏大、无功功率偏大的支路和电压裕度偏低的母线,将F中的信息权重作为相应因子的影响因数,将薄弱因子及其影响因数共同作为支路薄弱原因。综上,本文方法可实现薄弱支路辨识与溯因分析,全部流程如图 5所示。
3. 算例分析
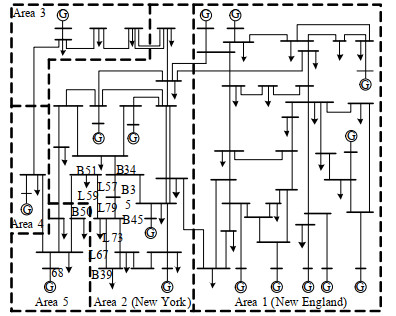
以IEEE68系统为例分析模型的辨识准确性、拓扑泛化性和辨识结果的有效性,以IEEE68、实际系统为例分析溯因方法的有效性。IEEE68系统含83条支路(如图 6所示),总发电量、总负荷量为1440MW、1424MW。如1.3节所述,生成不同拓扑结构,并将发电、负荷及无功补偿装置处的注入功率在80%至130%间均分为8层并加入±10%的随机波动,构建3种样本集如表 2所示。
表 2 GCNII模型的样本集Table 2. Sample sets for GCNII model样本集 开断支路 拓扑种类 功率层数 每层功率注入方式 运行方式 A 0 1 8 200 1600 B 1 67 8 40 21 440 C 2 2029 8 3 48 696 使用样本训练模型,设置第z类薄弱程度对应的损失函数权重值 {\omega _z} 为
{\omega _z} = \frac{1}{C}\frac{N}{{{n_z}}} + {k_z}{\text{ , }}z = 1,...,8 (13) 式中:C、N分别为薄弱程度类别总数和样本总数;nz、kz表示第z类薄弱度的样本数与变异系数。各薄弱度类别对应的样本数量占比和损失函数权重值如表 3所示。
表 3 8种薄弱程度类别的样本数量和损失权重Table 3. Sample proportion and loss weight of eight weakness categories类别 A B C ω 1 17.50% 16.70% 14.50% 0.9167 2 16% 15.20% 13.50% 0.9745 3 15.50% 15.50% 15% 0.8433 4 14% 15.30% 15% 0.8757 5 14% 14.10% 16% 0.8891 6 11.50% 11.30% 13.50% 1.07727 7 8% 8.20% 8.50% 1.5188 8 3.50% 3.70% 4% 3.2732 为分析模型的辨识准确性和拓扑泛化性,以5种数据驱动方法为对照:逻辑回归(logistic regression,LR)、支持向量机(support vector machines,SVM)、XGBoost (extreme gradient boosting,XGB)、深度神经网络(deep neural network,DNN)和GCN网络。横向拼接XGCNII与表征支路开断状态的特征 {X^t} \in {[0,1]^{83 \times 1}} ,生成非图模型的输入特征 {X^{{\text{cont}}}} \in {R^{83 \times 7}} 。XGB模型含80个树;DNN模型包括4层全连接层,分别含64、128、256、8个神经元;GCN模型含3层图卷积层。GCNII、GCN由Pytorch-Geometric实现,其余算法由Pytorch实现,连锁故障仿真由Matlab实现。
3.1 基于已知拓扑的辨识准确性测试
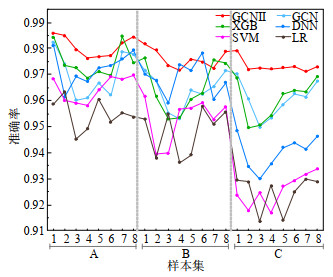
将表 2中的3个样本集按(5:2:3)的比例各自划分为训练集、验证集、测试集。上述6种数据驱动模型对A、B、C样本集中8种薄弱程度类别的辨识准确率如图 7所示,其中GCNII对8种薄弱度类别的辨识准确率均高于其他模型,达到97.5%以上;同一样本集内,GCNII的8种辨识准确率的离散程度均低于其他模型;随着样本拓扑结构差异的增大,SVM、LR、XGB、DNN、GCN在8种辨识准确率中的最低值由样本集A至C分别下降了4.332%、3.01%、1.79%、3.532%、1.02%,而GCNII仅下降0.612%,因此GCNII模型的辨识准确性较高、拓扑适应性较好。
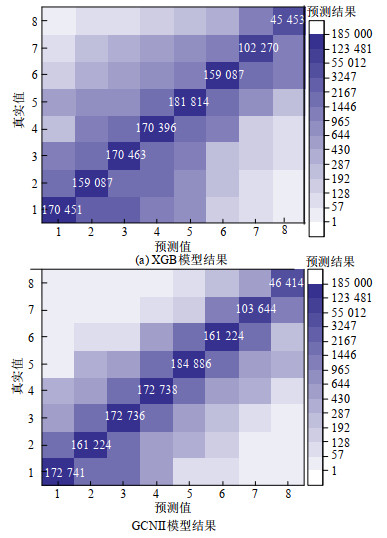
选取图 7中准确率较高的XGB和GCNII,对比其辨识结果距真实值的偏差程度。基于样本集C的测试结果混淆矩阵如图 8所示,相比于XGB,GCNII模型的输出值距真实值偏差更小,故GCNII模型辨识结果产生的误导性较低。
以遍历仿真法为对照分析同一潮流状态下本文方法的计算用时,遍历仿真法由1.3节中的连锁故障仿真和支路薄弱度划分环节组成。分析表 4可知,本文方法主要由离线环节承担计算压力,其在线用时显著低于遍历仿真法,达到1s以下。故在多点随机性变化的电网中,本文方法较易满足连锁故障预警和溯因分析对计算速度的要求。
表 4 遍历仿真方法与GCNII模型方法的计算时间对比Table 4. Computation time of simulation method and GCNII model方法类型 计算时间/s 遍历连锁故障仿真 49 模型辨识环节 0.0714 模型训练环节(数据集C) 781 溯因分析环节(某薄弱支路辨识结果) 0.82 3.2 基于未知拓扑的泛化能力测试
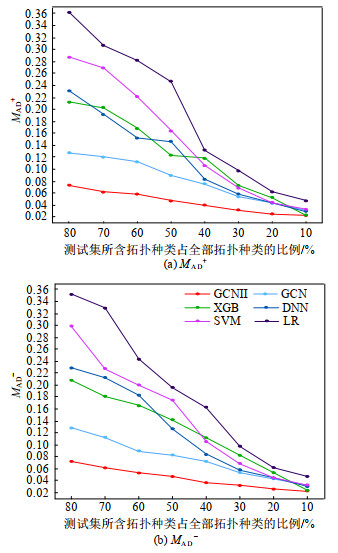
以上述5种数据驱动方法为对照,分析GCNII模型的拓扑泛化能力。用拓扑结构未参与训练的样本进行测试,按拓扑种类占比的不同将样本集C划分为8组训练、测试集。构建正、负偏差指标MAD+、MAD−,分别考察模型误判、漏判程度,以反映模型辨识准确性,偏差指标如下所示:
{M_{AD}}^ + = \frac{{\sum |y_{{\text{pred}}}^i - y_{{\text{lable}}}^i|}}{N}{\text{ , }}y_{{\text{pred}}}^i{{ \gt }}y_{{\text{lable}}}^i (14) {M_{{\text{AD}}}}^ - = \frac{{\sum |y_{{\text{pred}}}^i - y_{{\text{lable}}}^i|}}{N}{\text{ , }}y_{{\text{pred}}}^i{{ \lt }}y_{{\text{lable}}}^i (15) 式中:y_{{\text{pred}}}^i、y_{{\text{lable}}}^i为节点i的模型输出值、真实值;N为测试节点总数,测试结果如图 9所示。
由图 9可知,在8组训练、测试集中,GCNII模型的误判、漏判程度均低于其他模型;随着已知拓扑的减少和未知拓扑的增加,GCNII的MAD+、MAD−增幅明显小于其他模型,辨识准确性变化较少,故GCNII模型的拓扑泛化性较好。
3.3 模型辨识效果分析
以潮流介数法为对照,分析GCNII辨识结果的有效性。根据文献[40]、本文模型结构分别构建潮流介数法、本文方法的支路薄弱度评估指标如式(16)、(17)所示(以下简称介数指标、模型指标):
T_k^{{\text{Betw}}} = \sum\limits_{m \in G} {\sum\limits_{n \in L} {|\min ({P_m},{P_n}){I_k}(m,n)|\frac{{{P_k}}}{{{P_{k,{\text{max}}}}}}} } (16) {T}_{k}^{\text{GCNII}}={y}_{k}{h}_{k} ,\text{ }{y}_{k}=1,\mathrm{...},8 (17) 式中:TkBetw、TkGCNII为支路k的介数指标、模型指标;G、L为发电、负荷母线集合;Pm、Pn为母线m、n处的发电、负荷有功功率;Ik=(m, n)为母线对(m, n)的单位注入电流途经支路k的分量;Pk、Pk, max为支路k的有功功率及热稳定极限值;yk为支路k的GCNII模型输出结果,hk为softmax层中与yk对应神经元的输入值。用连锁故障负荷损失作为表征支路真实薄弱度的检验指标。
全网支路在3种指标下的排序结果从第5位开始不同。分析检验指标排第5—10位的支路(表 5)可知,其模型指标与检验指标大致相符,但L57、L79、L59的介数指标排名显著低于检验指标。上述支路的有功功率较低,分别为20MW、19.6MW、80MW,其对应的发电负荷母线对较少,由式(16)知介数指标值较小,与较高的真实薄弱度不符。
表 5 介数指标、模型指标、检验指标的排序结果Table 5. Ranking results of TkBetw、TkGCNIIand verify index支路
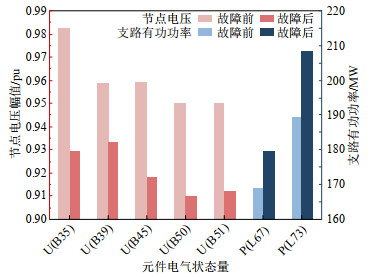
编号检验指标 辨识模型方法 潮流介数方法 负荷损失/MW 排序 模型指标 排序 介数指标 排序 75 432 5 5.466 5 0.026 37 5 59 412.28 6 4.95 7 0.003 62 74 57 410.4 7 4.884 6 0.003 48 75 39 403.2 8 4.272 8 0.028 36 6 21 380.16 9 4.154 9 0.022 46 8 79 372.84 10 4.092 10 0.005 27 47 以L57为例,由其开断后的部分元件状态可知(元件位置、状态量分别如图 6、10所示),L57断线并未大幅增加功率转移路径(L73、L67)的有功功率,但使5处母线电压跌落至0.95pu以下,其中B50、B51电压在故障前已接近0.95pu,故L57对该处电压具有较强的支撑作用,此故障模式凸显了考察静态电压安全特征的必要性。
由上述可知,潮流介数法关注支路承担功率传输任务的深度和广度,对低负载支路的电压支撑属性考察较少;本文方法不仅包含有功功率特征,还通过聚合电压裕度、支路无功功率等特征,计及对母线电压安全特性和支路电压支撑水平的考察,有助于减少辨识结果的遗漏。
3.4 薄弱支路的溯因分析
以IEEE68、实际系统为例,对模型辨识所得薄弱支路进行溯因分析,通过对照原始数据、对比校正效果,分析溯因方法所得薄弱因子及其影响因数对表征支路薄弱原因、指导预防控制的应用效果。
3.4.1 计及新能源出力波动的薄弱支路溯因分析
基于IEEE68系统模拟新能源出力波动场景。设B55、B60处发电机为风电机组,新能源渗透率为26.4%,参考文献[41]采用拉丁超立方抽样法(Latin hypercube sampling,LHS)生成风电出力;在B4与B30间加入高压直流输电支路,参考文献[42]采用节点功率注入方法对高压直流输电(high voltage direct current,HVDC)建模,引入HVDC的有功、无功约束,采用整流侧定变比、定电流和逆变侧定变比、定控制角的控制模式。
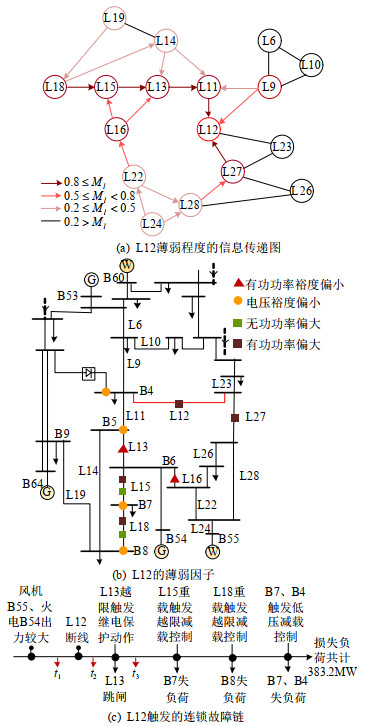
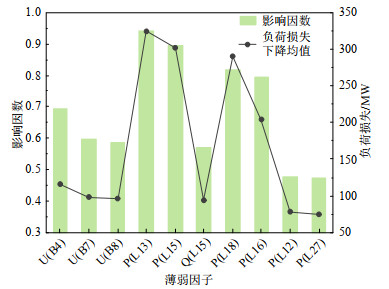
某工况下模型辨识得L12为第6类薄弱度支路,按阈值0.2筛选并保留高信息权重的边以提取关键节点如图 11(a)所示,按阈值0.5提取高影响因数的薄弱因子如图 11(b)所示,事故链如图 11(c)所示。
由图 11(a)、(c)知,信息权重较大的节点与故障过程的关联更为密切,如L13的跳闸和L15、L18的越限减载,故所提取的关键节点较为合理。
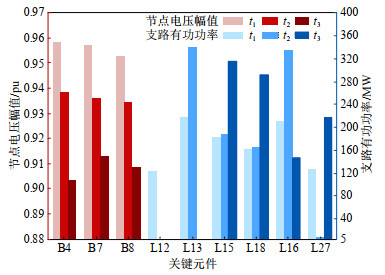
图 11(c)中3个故障时刻下部分元件状态量如图 12所示,结合图 11(b)分析薄弱因子与故障环节的关联关系。t1至t3的故障环节中,L12断线后,B55至B4的功率由(L27-L12)转移至(L16-L13),造成L13跳闸,扩大了事故规模。由薄弱因子知,L12、L27较大的有功功率在转移时的冲击强度较高;L13、L16负载率较高表明该支路剩余传输容量较低,在转移功率汇入时更易跳闸。故上述4个薄弱因子均与相继跳闸事故的推动因素相关。
t3后的故障环节中,L12-L13相继开断后,转移功率汇入L15、L18时触发支路越限减载,引发B4、B7、B8电压跌落而减载。由薄弱因子知,L15、L18的有功较大,表明该支路更易因转移功率的汇入而产生较大的减载损失;上述支路无功较大,且B4、B5、B7、B8的电压裕度偏低,表明此处电压在支路压降增加时更易跌至0.95pu以下。故上述8个薄弱因子均与减载损失的主导因素相关。因此,薄弱因子可较准确地还原故障链演化的推动因素。
对各薄弱因子进行单独校正,用校正后原故障下的负荷损失改变量描述因子的校正效果与贡献程度,以评估影响因数对因子贡献度的表征作用。
基于潮流优化实现校正控制,设控制变量为发电机有功功率、补偿电容容量和高压直流输电电流[41]。降低“有功功率裕度”“有功功率”因子对应支路的有功功率(以支路i为例),使其满足:
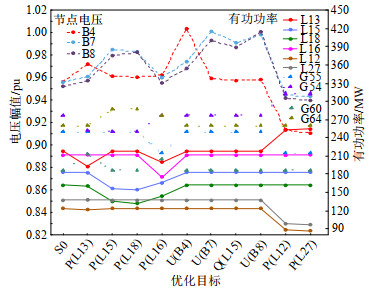
{P_i} + {P_{12 - i}} \lt k{P_{i,\max }} (18) 式中:P12-i为L12对支路i的转移功率;Pi、Pi, max为支路i的有功功率、继电保护阈值。“有功功率裕度”与支路跳闸概率相关,设其k值为0.95;“有功功率”与功率转移的冲击强度和支路压降有关,经数值分析与优化对比,设其k值为0.85。对“无功功率”因子对应支路的末端母线进行无功补偿,直至支路压降绝对值小于0.01pu;对“电压裕度”因子对应母线进行无功补偿直至电压幅值高于0.99pu。溯因分析结果中各薄弱因子的影响因数值如图 13柱状图所示,校正结果在原故障仿真下的负荷损失改变量如图 13点线图所示,校正结果中各元件状态量如图 14所示。
由图 13可知,校正高因数因子可更显著地降低支路薄弱程度,校正目标的影响因数与校正效果排名基本一致,故影响因数可较明确地刻画因子的贡献程度。
由图 14可知,仅降低薄弱支路自身功率时,在可行域内增加了G54出力,该功率途经L13,挤占了L12功率转移路径的传输容量,L12-L13相继跳闸依然存在,故障过程没有变化;仅校正因数最大的“L13有功”时,消除了相继跳闸的隐患,但未涉及电压的优化,电压跌落和减载损失依然存在。故当预防控制缺乏因子的指导时,可能存在加重薄弱因子消极影响的盲目反调、误调情况;当忽略低影响因数的因子时,存在优化不够彻底的局限性。
因此,各薄弱因子均具备信息价值,影响因数可较明确地表征因子的贡献程度,所构建的薄弱原因与机理认知所得结论较为相符;针对该原因实施预防控制,可避免部分因子的夸大和关键因子的误筛,有助于提升连锁故障预防控制的效果。
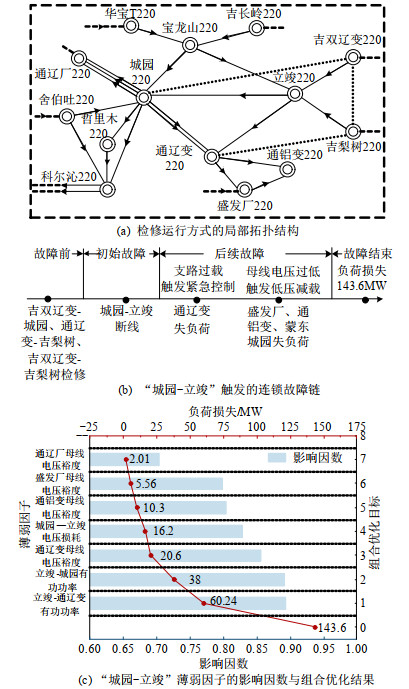
3.4.2 计及检修场景的薄弱支路溯因分析
基于蒙东局部电网模拟检修场景,如图 15(a) 所示。检修运行方式下,原吉双辽变-城园、吉梨树–通辽变的有功转移至互为替代输电通道的立竣-通辽变、立竣-城园。模型辨识得立竣-城园为第5类薄弱支路,事故链如图 15(b)所示,所得薄弱因子和影响因数如图 15(c)柱状图所示。
由图 15(a)、(b)知,立竣–城园开断后,转移功率使立竣–通辽变越限并触发减载,使通辽变、通铝变等母线触发低压减载。薄弱因子中,立竣–城园、立竣–通辽变作为开断支路与功率转移路径,其较大的有功功率更易提高越限减载的损失程度;通辽变作为转移功率汇入的母线,其较低的电压更易随立竣–通辽变压降的增加而跌至安全值以下,并波及邻近的低电压母线(通铝变等)。上述薄弱因子均与减载损失的主导因素相关。
考察薄弱因子的组合效应,将因子Xj按影响因数递减排序并逐一加入组合优化目标Cj=[X1, …, Xj](j=1, …, 7),各优化结果在原故障仿真下的负荷损失量如图 15(c)中点线图所示。分析可知,对高因数的因子进行组合校正可更显著地降低支路薄弱度,当可调节资源有限时,可按s因子影响因数的排序进行优化目标的配置。
综上所述,薄弱因子及其影响因数可较准确地描述促使薄弱支路形成的主导因素与贡献程度,因二者本质上是对辨识模型信息挖掘过程的提炼和展示,故知该模型可较有效地提取相应关键特征。溯因方法所得结论具备以下应用前景。
1)辨识结果的可信性评估:将溯因结论与直观经验进行对比,辅以连锁故障仿真和因子校正检验,评估模型辨识结果的可信性。
2)隐含规律的挖掘:将经检验的薄弱支路辨识结果与溯因结论存储为经验集,结合模式分析方法挖掘隐含规律,以丰富现有的运行经验。
4. 结论
利用图深度学习和解释方法实现了基于拓扑结构和潮流状态的薄弱支路辨识与溯因分析,所提方法具有以下优越性。
1)辨识模型在非欧空间中基于特征提取评估支路薄弱程度,IEEE68系统的测试结果表明,模型的在线用时较少,辨识速度较快,模型在未知拓扑结构下的误判、漏判指标较低,拓扑泛化性较好。
2)辨识模型采用改进的图卷积神经网络搭建信息感知域较大的深层模型,模型在IEEE68系统的测试准确率较高,辨识准确性较好。
3)溯因分析方法的算例结果表明,该方法提取的薄弱因子和影响因数与机理认知所得结论较为相符,可较准确地表征促使薄弱支路形成的主导因素及其贡献程度,并为支路薄弱原因的分析和连锁故障预防控制提供较有效的指导。
未来可结合显著子图挖掘提升模型的拓扑泛化性,结合电网运行经验提升溯因方法的适用性。
-
表 1 薄弱程度的划分
Table 1 Partitioning of weakness
薄弱程度 连锁故障事故后果 薄弱程度 连锁故障事故后果 1 无失负荷情况 5 0.15 < Lcut≤0.2 2 0 < Lcut≤0.05 6 无孤岛产生且Lcut > 0.2 3 0.05 < Lcut≤0.1 7 有孤岛产生且Lcut > 0.2 4 0.1 < Lcut≤0.15 8 潮流崩溃 表 2 GCNII模型的样本集
Table 2 Sample sets for GCNII model
样本集 开断支路 拓扑种类 功率层数 每层功率注入方式 运行方式 A 0 1 8 200 1600 B 1 67 8 40 21 440 C 2 2029 8 3 48 696 表 3 8种薄弱程度类别的样本数量和损失权重
Table 3 Sample proportion and loss weight of eight weakness categories
类别 A B C ω 1 17.50% 16.70% 14.50% 0.9167 2 16% 15.20% 13.50% 0.9745 3 15.50% 15.50% 15% 0.8433 4 14% 15.30% 15% 0.8757 5 14% 14.10% 16% 0.8891 6 11.50% 11.30% 13.50% 1.07727 7 8% 8.20% 8.50% 1.5188 8 3.50% 3.70% 4% 3.2732 表 4 遍历仿真方法与GCNII模型方法的计算时间对比
Table 4 Computation time of simulation method and GCNII model
方法类型 计算时间/s 遍历连锁故障仿真 49 模型辨识环节 0.0714 模型训练环节(数据集C) 781 溯因分析环节(某薄弱支路辨识结果) 0.82 表 5 介数指标、模型指标、检验指标的排序结果
Table 5 Ranking results of TkBetw、TkGCNIIand verify index
支路
编号检验指标 辨识模型方法 潮流介数方法 负荷损失/MW 排序 模型指标 排序 介数指标 排序 75 432 5 5.466 5 0.026 37 5 59 412.28 6 4.95 7 0.003 62 74 57 410.4 7 4.884 6 0.003 48 75 39 403.2 8 4.272 8 0.028 36 6 21 380.16 9 4.154 9 0.022 46 8 79 372.84 10 4.092 10 0.005 27 47 -
[1] 谭玉东, 李欣然, 蔡晔, 等. 基于动态潮流的电网连锁故障模型及关键线路识别[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35(3): 615-622. http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwa5QAVQroAGzve%2BMXEZ%2Bd4okGD2NMA%2BYpYBZAoQr7SeB?encrypt=1 TAN Yudong, LI Xinran, CAI Ye, et al. Modeling cascading failures in power grid based on dynamic power flow and vulnerable line identification[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35(3): 615-622(in Chinese). http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwa5QAVQroAGzve%2BMXEZ%2Bd4okGD2NMA%2BYpYBZAoQr7SeB?encrypt=1
[2] 蔡晔, 曹一家, 李勇, 等. 考虑电压等级和运行状态的电网脆弱线路辨识[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34(13): 2124-2131. DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.13.014 CAI Ye, CAO Yijia, LI Yong, et al. Identification of vulnerable lines in urban power grid based on voltagegrade and running state[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34(13): 2124-2131(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.13.014
[3] 曾辉, 孙峰, 李铁, 等. 澳大利亚"9·28"大停电事故分析及对中国启示[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41(13): 1-6. DOI: 10.7500/AEPS20170120002 ZENG Hui, SUN Feng, LI Tie, et al. Analysis of "9·28" blackout in South Australia and its enlightenment to China[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41(13): 1-6(in Chinese). DOI: 10.7500/AEPS20170120002
[4] 李保杰, 李进波, 李洪杰, 等. 土耳其"3.31"大停电事故的分析及对我国电网安全运行的启示[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36(21): 5788-5795. http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwUENYoFxgOawcvRjYrgN7hqUIwks%2BPbDG1CPNZa%2BFmFw?encrypt=1 LI Baojie, LI Jinbo, LI Hongjie, et al. Analysis of Turkish blackout on March 31, 2015 and lessons on China power grid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(21): 5788-5795(in Chinese). http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwUENYoFxgOawcvRjYrgN7hqUIwks%2BPbDG1CPNZa%2BFmFw?encrypt=1
[5] 李勇, 刘俊勇, 刘晓宇, 等. 基于潮流熵测度的连锁故障脆弱线路评估及其在四川主干电网中的应用[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2013, 33(10): 40-46. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6047.2013.10.007 LI Yong, LIU Junyong, LIU Xiaoyu, et al. Vulnerability assessment based on power flow entropy for lines in cascading failures and its application in Sichuan backbone power grid[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2013, 33(10): 40-46(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6047.2013.10.007
[6] 刘威, 张东霞, 丁玉成, 等. 基于随机矩阵理论与熵理论的电网薄弱环节辨识方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37(20): 5893-5901. DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.170212 LIU Wei, ZHANG Dongxia, DING Yucheng, et al. Power grid vulnerability identification methods based on random matrix theory and entropy theory[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(20): 5893-5901(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.170212
[7] 黄昭蒙, 李华强, 杜涛, 等. 基于支路能量函数的脆弱支路评估[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2012, 40(15): 7-11, 115. DOI: 10.7667/j.issn.1674-3415.2012.15.002 HUANG Zhaomeng, LI Huaqiang, LI Tao, et al. Vulnerable branch assessment based on branch energy function[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2012, 40(15): 7-11, 115(in Chinese). DOI: 10.7667/j.issn.1674-3415.2012.15.002
[8] 曾凯文, 文劲宇, 程时杰, 等. 复杂电网连锁故障下的关键线路辨识[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34(7): 1103-1112. DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.07.012 ZENG Kaiwen, WEN Jinyu, CHENG Shijie, et al. Critical line identification of complex power system in cascading failure[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34(7): 1103-1112(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2014.07.012
[9] ZHANG Qiao, FAN Wenli, QIU Ziyang, et al. A new identification approach of power system vulnerable lines based on weighed H-index[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 121421-121431. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2937903
[10] QI Junjian, MEI Shengwei, LIU Feng. Blackout model considering slow process[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2013, 28(3): 3274-3282. DOI: 10.1109/TPWRS.2012.2230196
[11] ROCCHETTA R, PATELLI E. Assessment of power grid vulnerabilities accounting for stochastic loads and model imprecision[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2018, 98: 219-232. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142061517313571
[12] 苏慧玲, 李扬. 基于电力系统复杂网络特征的线路脆弱性风险分析[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2014, 34(2): 101-107. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6047.2014.02.018 SU Huiling, LI Yang. Line vulnerability risk analysis based on complex network characteristics of power system[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2014, 34(2): 101-107(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6047.2014.02.018
[13] GUPTA S, KAZI F, WAGH S, et al. Analysis and prediction of vulnerability in smart power transmission system: a geometrical approach[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2018, 94: 77-87. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142061516315472
[14] POUDEL S, NI Zhen, SUN Wei. Electrical distance approach for searching vulnerable branches during contingencies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, 2018, 9(4): 3373-3382. DOI: 10.1109/TSG.2016.2631622
[15] 刘文颖, 梁才, 徐鹏, 等. 基于潮流介数的电力系统关键线路辨识[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2013, 33(31): 90-98. DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2013.31.012 LIU Wenying, LIANG Cai, XU Peng, et al. Identification of critical line in power systems based on flow betweenness[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33(31): 90-98(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2013.31.012
[16] 许立雄, 刘俊勇, 丁理杰, 等. 基于网络流介数的关键线路识别[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2013, 41(5): 91-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDQW201305017.htm XU Lixiong, LIU Junyong, DING Lijie, et al. Identification of critical lines in power grid based on network flow betweenness[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2013, 41(5): 91-96(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDQW201305017.htm
[17] FAN Wenli, ZHANG Xuemin, MEI Shengwei, et al. Vulnerable transmission line identification using ISH theory in power grids[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2018, 12(4): 1014-1020.
[18] EPPSTEIN M J, HINES P. A "random chemistry" algorithm for identifying collections of multiple contingencies that initiate cascading failure[J]. IEEE Transactions On Power Systems, 2012, 27(3): 1698-1705. DOI: 10.1109/TPWRS.2012.2183624
[19] ZHANG Zhimei, YAO Rui, HUANG Shaowei, et al. An online search method for representative risky fault chains based on reinforcement learning and knowledge transfer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2020, 35(3): 1856-1867. DOI: 10.1109/TPWRS.2019.2951171
[20] LIU Yuxiao, WANG Yi, YONG Pei, et al. Fast power system cascading failure path searching with high wind power penetration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2020, 11(4): 2274-2283. DOI: 10.1109/TSTE.2019.2953867
[21] 杨燕, 杨知方, 余娟, 等. 基于深度学习的含不确定性N−1安全校核方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41(8): 2716-2724. http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwTcGu2AcALFBBo0rkaGHPaoNylixdGu5v6dJ1Wf2DPAS?encrypt=1 YANG Yan, YANG Zhifang, YU Juan, et al. Fast analysis of N−1contingency screening with uncertainty scenarios based on deeplearning[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41(8): 2716-2724(in Chinese). http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwTcGu2AcALFBBo0rkaGHPaoNylixdGu5v6dJ1Wf2DPAS?encrypt=1
[22] 王铮澄, 周艳真, 郭庆来, 等. 考虑电力系统拓扑变化的消息传递图神经网络暂态稳定评估[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41(7): 2341-2349. http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwQgYwE5lyfUEjWtP7JYh9TgUFQA0ZvEt_f7v%2BY5yGUMy?encrypt=1 WANG Zhengcheng, ZHOU Yanzhen, GUO Qinglai, et al. Transient stability assessment of power system considering topological change: a message passing neural network-based approach[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41(7): 2341-2349(in Chinese). http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwQgYwE5lyfUEjWtP7JYh9TgUFQA0ZvEt_f7v%2BY5yGUMy?encrypt=1
[23] HUANG Jiyu, GUAN Lin, SU Yinsheng, et al. A topology adaptive high-speed transient stability assessment scheme based on multi-graph attention network with residual structure[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2021, 130: 106948.
[24] 杨梅, 刘俊勇, 刘挺坚, 等. 节点图和边图切换卷积驱动的快速静态安全分析方法[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45(6): 2070-2079. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DWJS202106004.htm YANG Mei, LIU Junyong, LIU Tingjian, et al. Switching convolution of node graph and line graph-driven method for fast static securityanalysis[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45(6): 2070-2079(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DWJS202106004.htm
[25] CHEN Kunjin, HU Jun, ZHANG Yu, et al. Fault location in power distribution systems via deep graph convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(1): 119-131. DOI: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2951964
[26] 陈明华, 刘群英, 张家枢, 等. 基于XGBoost的电力系统暂态稳定预测方法[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44(3): 1026-1033. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DWJS202003026.htm CHEN Minghua, LIU Qunying, ZHANG Jiashu, et al. XGBoost-based algorithm for post-fault transient stability status prediction[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44(3): 1026-1033(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DWJS202003026.htm
[27] 韩天森, 陈金富, 李银红, 等. 电力系统稳定评估机器学习可解释代理模型研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(13): 4122-4130. http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwSzWKcfrHCN1EHrc%2BjSKtN6aF8ig_i%2BKvL7_v9MHgrW3?encrypt=1 HAN Tiansen, CHEN Jinfu, LI Yinhong, et al. Study on interpretable surrogate model for power system stability evaluation machine learning[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(13): 4122-4130(in Chinese). http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwSzWKcfrHCN1EHrc%2BjSKtN6aF8ig_i%2BKvL7_v9MHgrW3?encrypt=1
[28] 周挺, 杨军, 詹祥澎, 等. 一种数据驱动的暂态电压稳定评估方法及其可解释性研究[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45(11): 4416-4425. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DWJS202111023.htm ZHOU Ting, YANG Jun, ZHAN Xiangpeng, et al. A data-driven method for transient voltage stability assessment and its interpretability analysis[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45(11): 4416-4425(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DWJS202111023.htm
[29] LIU Yuxiao, ZHANG Ning, WU Dan, et al. Guiding cascading failuresearch with interpretable graph convolutional network[J]. arXivpreprintarXiv: 2001.11553, 2020.
[30] 李卫东, 唐丽艳, 宋家骅. 电力系统运行模式结构特征提取方法的研究[J]. 中国电力, 1998, 31(4): 29-31, 80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDL804.007.htm LI Weidong, TANG Yanli, ZHU Jiahua. A methodology for extracting power system operational configuration characteristics[J]. Electric Power, 1998, 31(4): 29-31, 80(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDL804.007.htm
[31] CHEN Meng, WEI Zhewei, HUANG Zengfeng, et al. Simple and deep graph convolutional networks [C]//Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. JMLR. org, 2020: 161.
[32] OONOK, SUZUKIT. Graph neural networks exponentially lose expressive power for node classification[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations. Addis Ababa: OpenReview. net, 2020.
[33] 李文沅. 电力系统风险评估模型、方法和应用[M]. 周家启, 卢继平, 胡小正, 等, 译. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006: 75-107. LI Wenyuan. Risk assessment of power systems: models, methods, and applications[M]. ZHOU Jiaqi, LU Jiping, HU Xiaozheng, et al, trans. Beijing: Science Press, 2006: 75-107(in Chinese).
[34] 丁明, 钱宇骋, 张晶晶. 考虑多时间尺度的连锁故障演化和风险评估模型[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37(20): 5902-5912. http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwf4npkdJfVwXjMmmjy%2BEmmvY%2B161kD_tHq14Hjk0M6%2Br?encrypt=1 DING Ming, QIAN Yucheng, ZHANG Jingjing. Multi-timescale cascading failure evolution and risk assessment model[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(20): 5902-5912(in Chinese). http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwf4npkdJfVwXjMmmjy%2BEmmvY%2B161kD_tHq14Hjk0M6%2Br?encrypt=1
[35] 竺炜, 许珊, 尹军, 等. 电网的分散负荷安全域及其应用(一): 电网静态安全的线路负荷安全域[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41(8): 2691-2704. http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwVelQtGHyU2%2BUDEw%2BSncjkqjXVNixN7RFaNO4zfBNO_H?encrypt=1 ZHU Wei, XU Shan, YIN Jun, et al. Distributed load security domain and its application(Ⅰ): line load security domain for grid static security[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41(8): 2691-2704. http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwVelQtGHyU2%2BUDEw%2BSncjkqjXVNixN7RFaNO4zfBNO_H?encrypt=1
[36] 竺炜, 周孝信, 唐如. 电网的弹性力学网络拓扑映射[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2011, 31(31): 109-117. http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwSITd4dG9vsUhmz88lDdwVtc1HMBnz6OQFTV%2BpGl7sdQ?encrypt=1 ZHU Wei, ZHOU Xiaoxin, TANG Ru. Elasticity network topology mapping for power grid[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2011, 31(31): 109-117(in Chinese). http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwSITd4dG9vsUhmz88lDdwVtc1HMBnz6OQFTV%2BpGl7sdQ?encrypt=1
[37] NI Ming, MCCALLEY J D, VITTAL V, et al. Online risk-based securityassessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2003, 18(1): 258-265. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1178806/
[38] YING R, BOURGEOIS D, YOU Jiaxuan, et al. GNNExplainer: generating explanations for graph neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, 2019.
[39] ZINTGRAFL M, COHENT S, ADELT, et al. Visualizing deep neural network decisions: prediction difference analysis[C]//Proceedings of the5th International Conference on Learning Representations. Toulon: OpenReview. net, 2017.
[40] 庞华勇. 基于有功潮流介数和潮流熵的电网脆弱环节辨识[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2017. PANG Huayong. Identification of vulnerable links in power system based on active power flow betweenness and power flow entropy[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017(in Chinese).
[41] 赵福林. 考虑源荷波动的电网灵活性评估与风险调度研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2021. ZHAO Fulin. Research on flexibility assessment and risk dispatch of power grid considering source and load fluctuation[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2021(in Chinese).
[42] 江全元, 耿光超. 含高压直流输电系统的内点最优潮流算法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2009, 29(25): 43-49. http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwWqWEsPZGZmoca6Vx1ix1ly4LoG2qtcg14bEjriugAFL?encrypt=1 JIANG Quanyuan, GENG Guangchao. Interior-point optimal power flow with the high voltage direct current transmission system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2009, 29(25): 43-49(in Chinese). http://www.pcsee.org/x_iA9ig181GiGW7b5ocZwWqWEsPZGZmoca6Vx1ix1ly4LoG2qtcg14bEjriugAFL?encrypt=1




 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



